Your shopping cart is empty!
Your shopping cart is empty! Thyroid gland: diseases, their causes and methods of treatment
In 1656, the term “thyroid gland” was proposed by the English doctor Thomas Warton, who considered the thyroid gland to decorate the neck, designed to make it rounded.
In fact, the thyroid gland is iron secretion glands, in the cells of which hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) are produced, controlling metabolism and energy, growth processes, maturation of tissues and organs.
The thyroid hormones regulate the activity of the brain, nervous and cardiovascular system, the gastrointestinal tract, affect the reproductive function, the functioning of the mammary and sweat glands.
In case of violation of the thyroid gland, the following symptoms may appear:
lethargy, apathy;
loss of appetite, decreased body weight or vice versa, a sharp increase in body weight;
irritability, tearfulness;
sensation of heartbeat;
dry skin, hair loss;
violation of the menstrual cycle in women;
decrease in libido;
sweating, sleep problems;
swelling of the face, fingers, lower extremities;
decrease in memory and attention;
Hoarse voice, depressive condition and much more.
The most common thyroid pathologies:
diffuse euthyroid goiter;
autoimmune thyroiditis;
colloidal nodal goiter;
hypothyroidism;
multi -sized goiter;
thyrotoxicosis;
subacute thyroiditis.
In most cases, the thyroid gland does not need preventive control with an endocrinologist. If a person does not bother, then it is enough to undergo a dispensary examination by the therapist. After inspection, the therapist, if necessary, directs patients to consult an endocrinologist.
It is necessary to visit an endocrinologist yourself if you have a burdened family history for thyroid diseases or any other endocrine glands and if there are complaints.
How does an endocrinologist diagnose?
The endocrinologist will carefully collect the anamnesis, conduct a physical examination and palpation of the thyroid gland. If necessary, prescribe laboratory and instrumental research. According to the testimony - consultation of other specialists.
Laboratory analyzes include:
Hormonal examination (TSH, Free T4, Free T3, AT to TPO, TG, AT K, AT K RTTG and others) - are prescribed only after examination by the doctor with an endocrinologist!
Clinical blood test (according to indications)
Biochemical blood test (according to indications)
The instrumental methods of thyroid examination include:
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland,
Scintigraphy of the thyroid gland
Thin -iginal aspiration biopsy of the thyroid gland.
Treatment of thyroid gland. Methods
Treatment of thyroid diseases includes:
conservative treatment (therapy with iodine preparations, replacement therapy with sodium levotyroxin, anti -icine drugs, glucocorticoids);
surgical (removal of the thyroid gland - thyroidctomy);
Radiation therapy - treatment with radioactive iodine.
What are the causes of diseases and how to prevent the disease?
The causes of thyroid diseases include:
iodine deficiency;
hereditary predisposition (genetic changes);
taking some drugs;
Environmental factors.
The most common cause is iodine deficiency, it has numerous negative consequences regarding the development and formation of the human body, especially at the stage of intrauterine development and in early childhood.
The iodine deficiency in nutrition leads to the development of the following thyroid diseases:
diffuse non -toxic goiter, nodal/multi -sized goiter;
thyrotoxicosis due to the functional autonomy of the thyroid gland/toxic adenoma of the thyroid gland;
Subclinical hypothyroidism due to iodine deficiency.
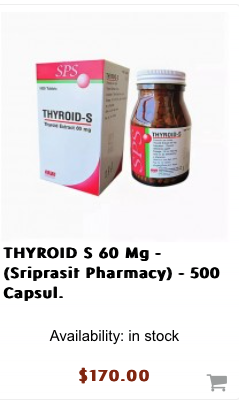
Buy Thyroid S 60 Mg - (Sriprasit Pharmacy) - 500 Tablets.